Fish diet heats up marine biodiversity hotspot
by Ale Siqueira/David Bellwood/Pete Cowman 21 Feb 2021 06:31 UTC
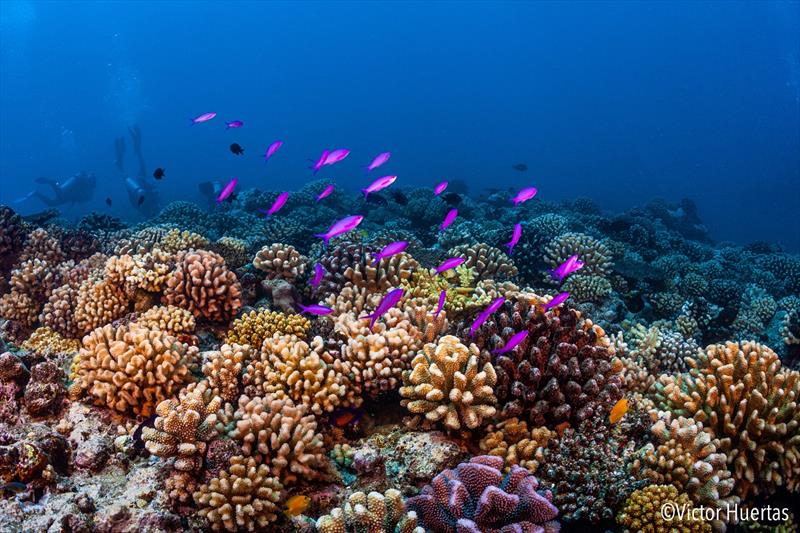

Planktivores (Pseudanthias pascalus) feeding above the coral reefs of French Polynesia. Planktivores are far more diverse than other fish species in the Indo-Australian Archipelago © Victor Huertas
Scientists have discovered a never-before-seen biodiversity pattern of coral reef fishes that suggests some fishes might be exceptionally vulnerable to environmental change.
A new study shows plankton-eating coral reef fishes (planktivores) are far more diverse than others in the Indo-Australian Archipelago, a global marine biodiversity hotspot.
The findings highlight, for the first time, a unique link between the diet and distribution of species across the marine realm.
"The archipelago is one of the most complex and dynamic geological regions in the tropics," said lead author Dr Ale Siqueira from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies at James Cook University (Coral CoE at JCU). "And its fishes underpin its status as a biodiversity hotspot."
"The exceptional success of planktivores may be a result of the hotspot's unique geological configuration and oceanographic currents, which ensure a constant and abundant source of planktonic food," said co-author Professor David Bellwood, also from Coral CoE at JCU.
"Such stable conditions over the past five million years are likely to have promoted the accumulation of planktivorous fish species in the hotspot."
While planktivores thrive in the hotspot, they have had a difficult history in more remote areas with the possibility of food shortages and periodic extinctions.
"Planktivore richness drops abruptly away from the marine hotspot—and more so than any of the other dietary categories studied," Dr Siqueira said.
These findings suggest a vulnerability of planktivorous coral reef fishes to environmental change, despite their species richness within the hotspot.
"We examined the global diversity patterns for more than 3,600 coral reef fishes," said co-author Dr Pete Cowman from Coral CoE at JCU and Queensland Museum.
Dr Cowman said the research identified a link between biodiversity, food and habitat—emphasising the importance of species interactions with their environment.
"Understanding the ecosystem roles of different species and how they have changed through space and time offers the potential for exciting new insights, as revealed by our planktivores," Dr Cowman said.
Dr Siqueira said a deeper understanding of species interactions is needed.
"Future research should focus on the ecosystem roles that different species play," Dr Siqueira said.
"We need to describe changes in the roles of species through space and time, rather than simply documenting species and their numbers; the traditional approach in science."
Paper
Siqueira A, Morais R, Bellwood D, Cowman P. (2021). 'Planktivores as trophic drivers of global coral reef fish diversity'. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2019404118.